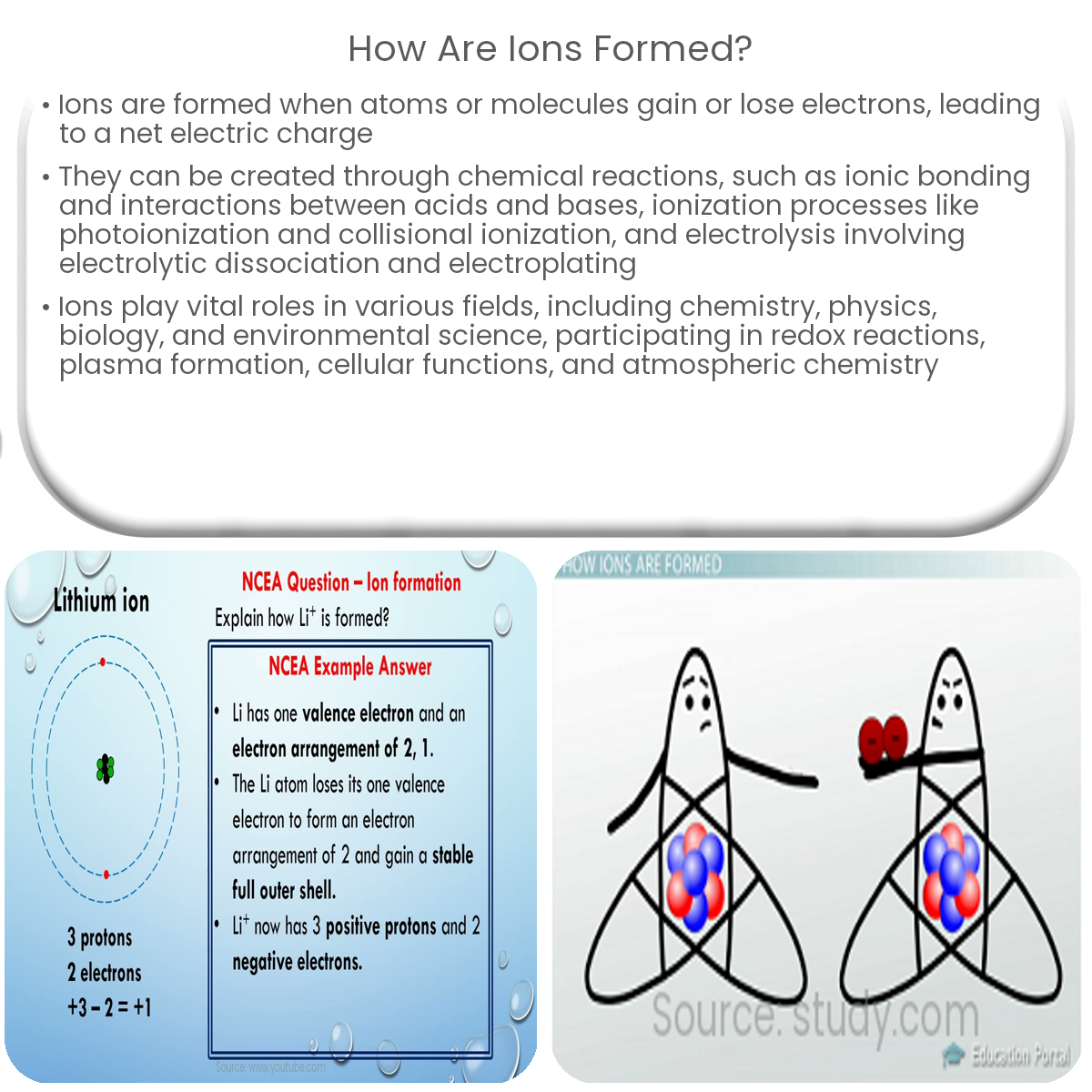
How Are Ions Formed - Ionic compounds are formed by ionic bonds from the electrostatic attraction of positively and negatively charged ions, generally between. Sulfuric acid is a strong acid that typically dissociates into hydronium ions and. Ions formed from sodium atoms have a charge of +1. Acids typically produce hydrogen ions (h+) when dissolved in water, which gives them their acidic properties. What ions are present in acids? Sodium easily loses one electron to achieve a. Use potassium (k) as an example. How many protons and electrons does a neutral. How are positive ions formed (what is gained or lost)? No, sulfuric acid does not have a dative bond.
How many protons and electrons does a neutral. Sodium easily loses one electron to achieve a. What ions are present in acids? Acids typically produce hydrogen ions (h+) when dissolved in water, which gives them their acidic properties. These ions are called cations. Ionic compounds are formed by ionic bonds from the electrostatic attraction of positively and negatively charged ions, generally between. Use potassium (k) as an example. Sulfuric acid is a strong acid that typically dissociates into hydronium ions and. No, sulfuric acid does not have a dative bond. How are positive ions formed (what is gained or lost)?
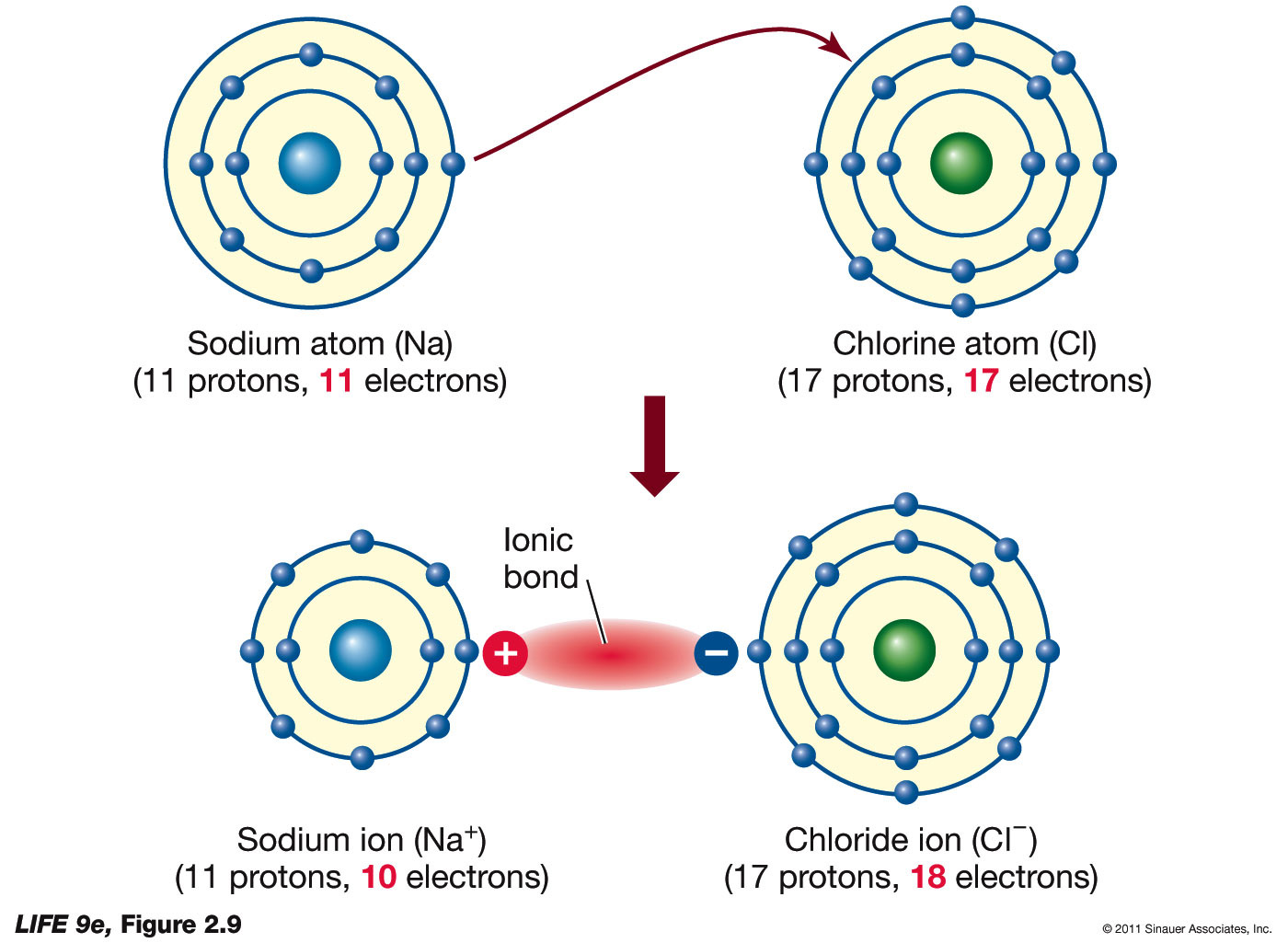
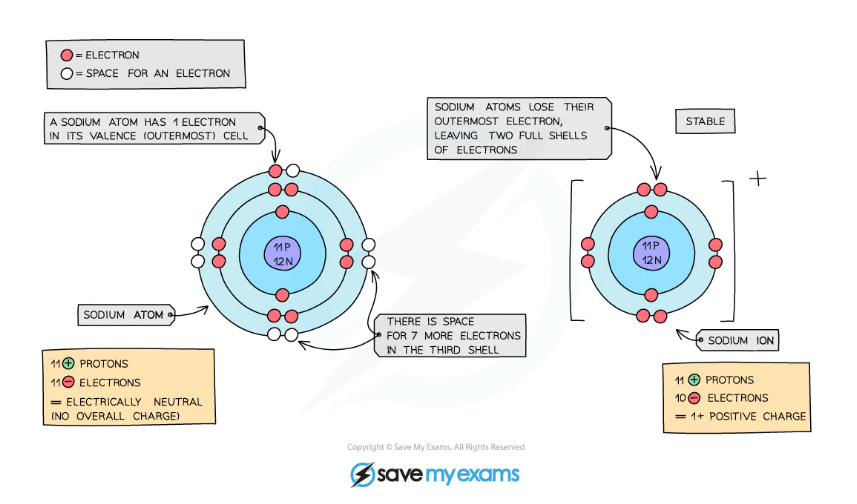
Ions formed from sodium atoms have a charge of +1. Ionic compounds are formed by ionic bonds from the electrostatic attraction of positively and negatively charged ions, generally between. Sodium easily loses one electron to achieve a. Sulfuric acid is a strong acid that typically dissociates into hydronium ions and. Use potassium (k) as an example. How are positive ions formed (what is gained or lost)? No, sulfuric acid does not have a dative bond. These ions are called cations. Acids typically produce hydrogen ions (h+) when dissolved in water, which gives them their acidic properties. What ions are present in acids?
Ion A Has A Structure Of In The Diagram Above Atom Molecule
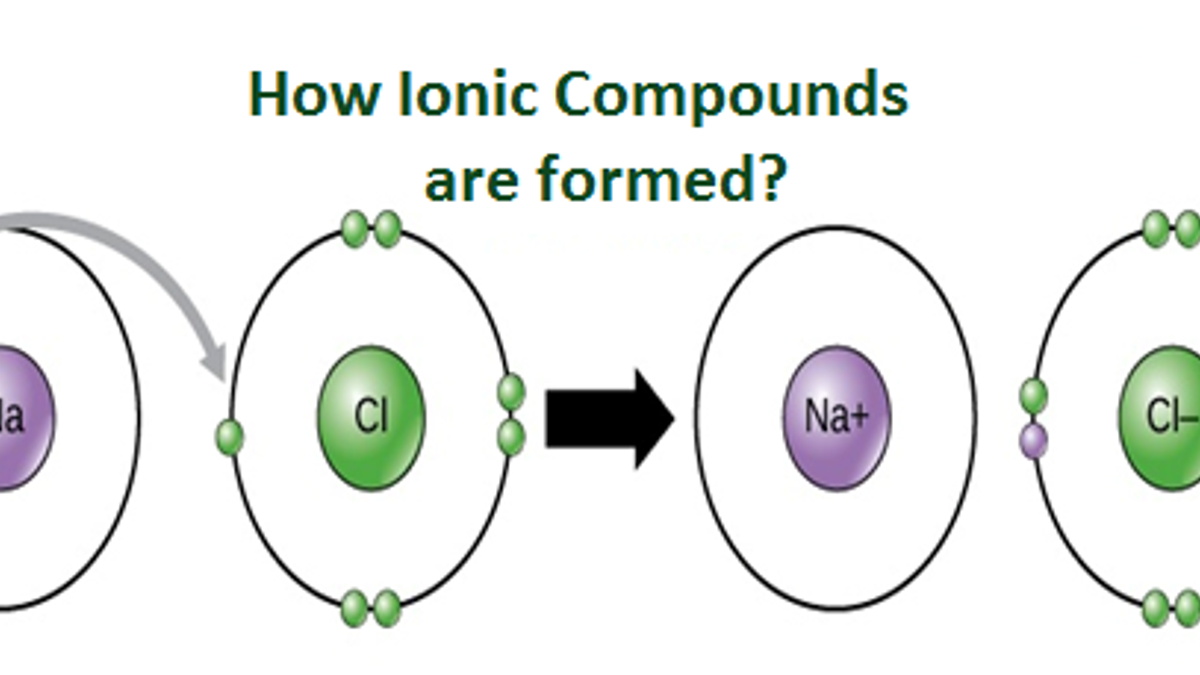
Ionic compounds are formed by ionic bonds from the electrostatic attraction of positively and negatively charged ions, generally between. No, sulfuric acid does not have a dative bond. These ions are called cations. Ions formed from sodium atoms have a charge of +1. Sodium easily loses one electron to achieve a.
Objectives Identify elements common to all living things Describe how
Ions formed from sodium atoms have a charge of +1. How many protons and electrons does a neutral. What ions are present in acids? Ionic compounds are formed by ionic bonds from the electrostatic attraction of positively and negatively charged ions, generally between. How are positive ions formed (what is gained or lost)?
EDEXCEL IGCSE CHEMISTRY DOUBLE SCIENCE 复习笔记:1.6.1 Formation of Ions
Ionic compounds are formed by ionic bonds from the electrostatic attraction of positively and negatively charged ions, generally between. Use potassium (k) as an example. Sulfuric acid is a strong acid that typically dissociates into hydronium ions and. What ions are present in acids? How are positive ions formed (what is gained or lost)?
What Is An Ion
How many protons and electrons does a neutral. Acids typically produce hydrogen ions (h+) when dissolved in water, which gives them their acidic properties. Ionic compounds are formed by ionic bonds from the electrostatic attraction of positively and negatively charged ions, generally between. These ions are called cations. Sulfuric acid is a strong acid that typically dissociates into hydronium ions.
Ion How Ions are Formed from Neutral Atoms of Different elements YouTube
What ions are present in acids? These ions are called cations. How many protons and electrons does a neutral. Sulfuric acid is a strong acid that typically dissociates into hydronium ions and. How are positive ions formed (what is gained or lost)?
Unit 4 Ions Two ions are talking to each other in solution. ppt download
What ions are present in acids? Sodium easily loses one electron to achieve a. Use potassium (k) as an example. How are positive ions formed (what is gained or lost)? These ions are called cations.
How are ions formed?
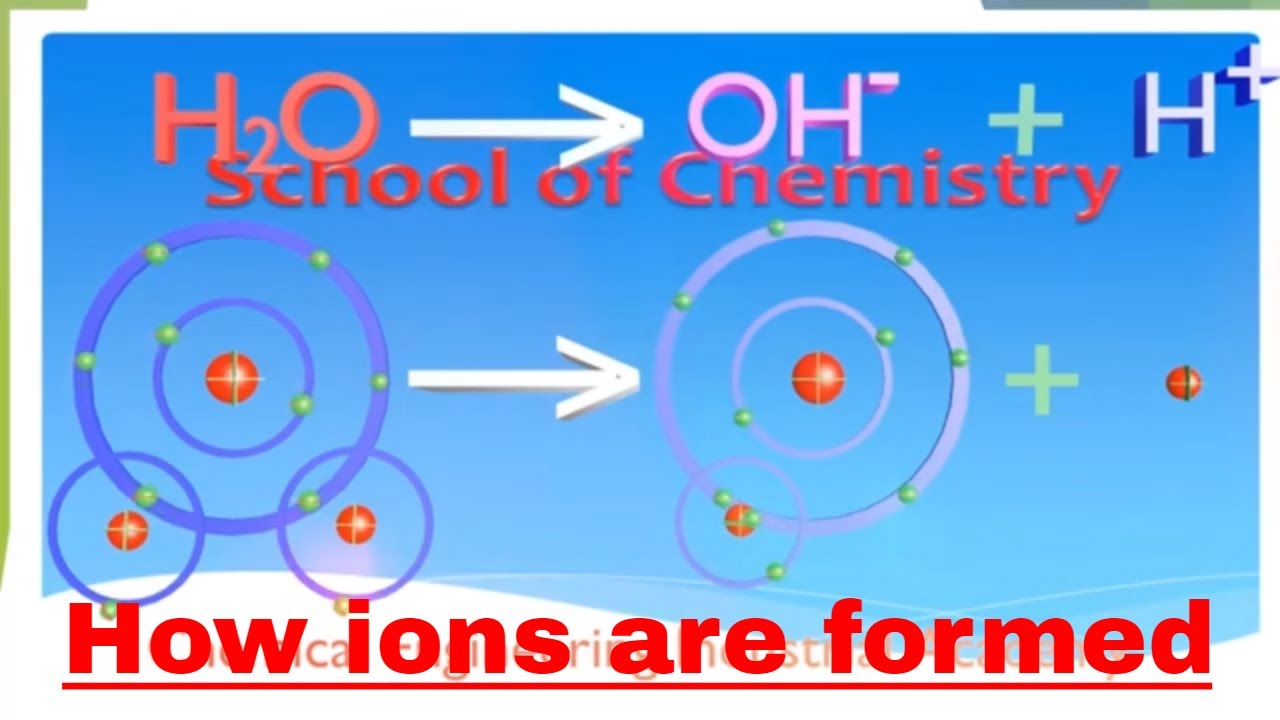
These ions are called cations. Acids typically produce hydrogen ions (h+) when dissolved in water, which gives them their acidic properties. No, sulfuric acid does not have a dative bond. Sodium easily loses one electron to achieve a. What ions are present in acids?
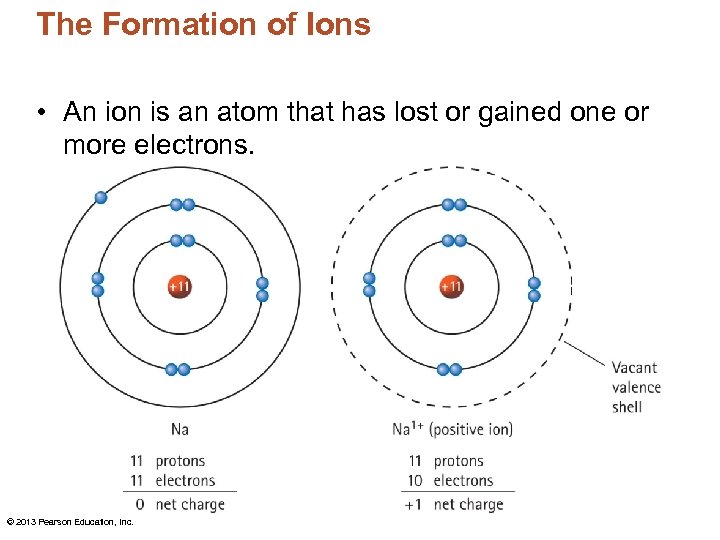
The Formation of Ions An ion is
How many protons and electrons does a neutral. Sodium easily loses one electron to achieve a. What ions are present in acids? Ionic compounds are formed by ionic bonds from the electrostatic attraction of positively and negatively charged ions, generally between. Ions formed from sodium atoms have a charge of +1.
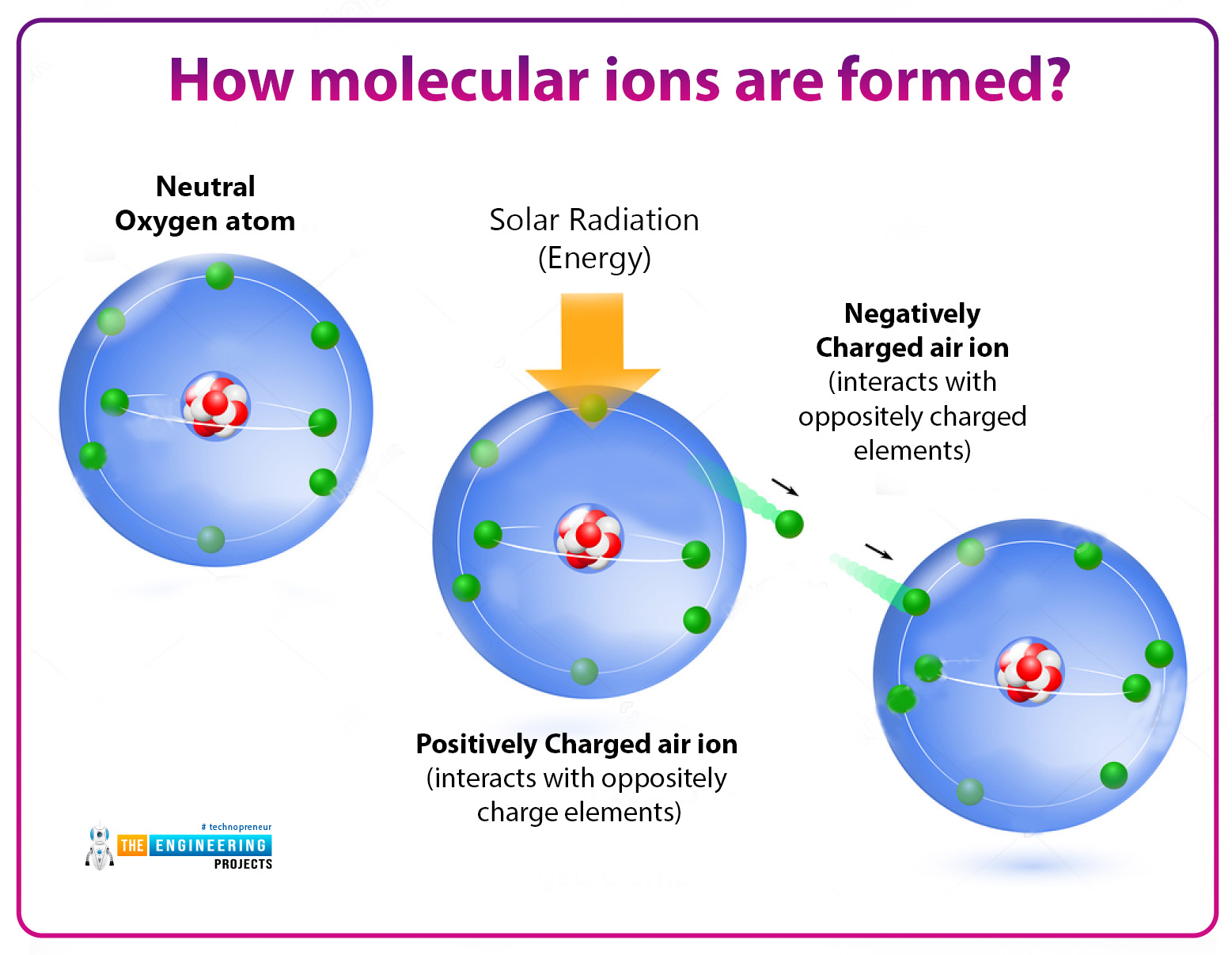
How Ions Are Formed? Infrared for Health
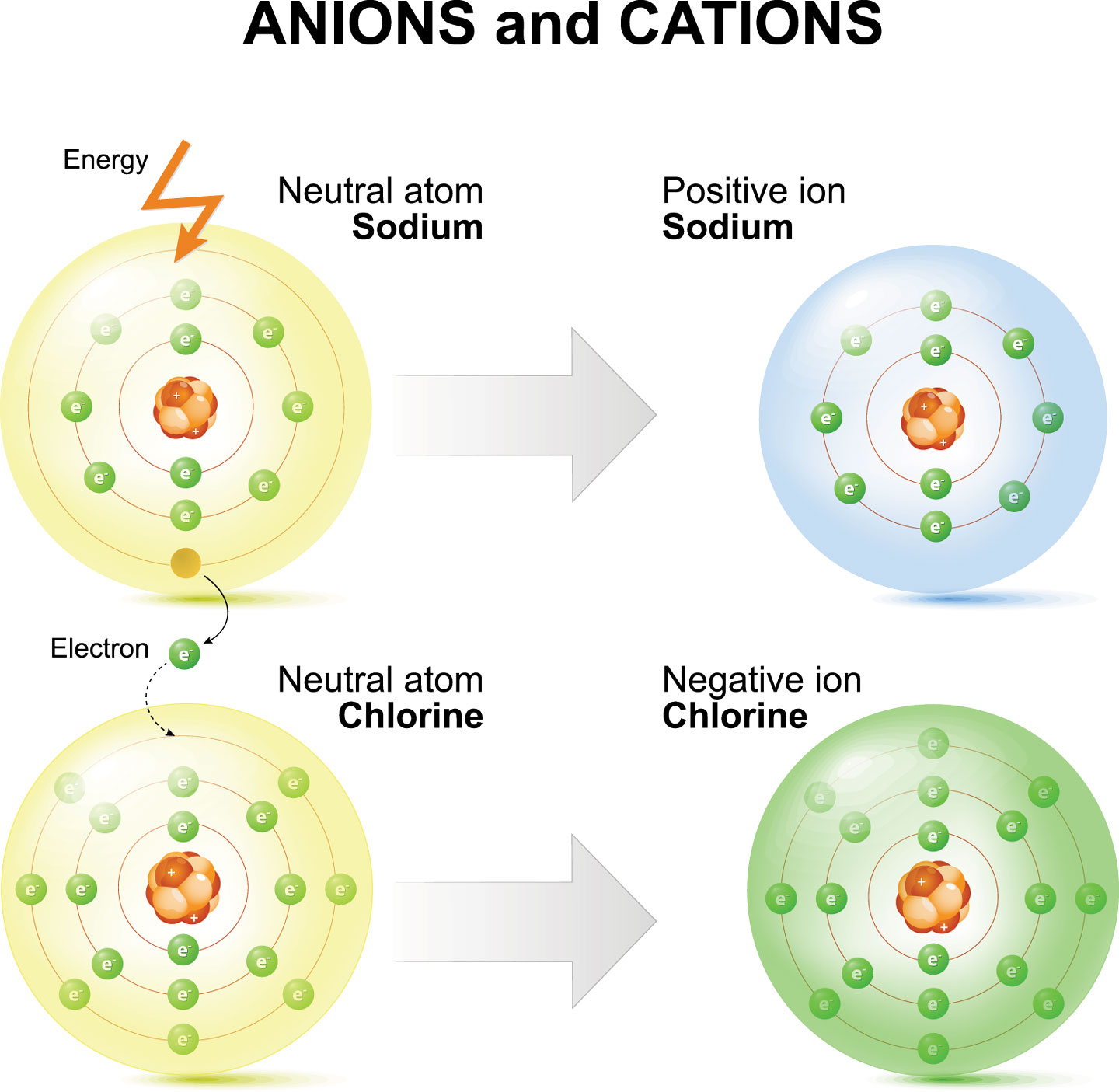
Ionic compounds are formed by ionic bonds from the electrostatic attraction of positively and negatively charged ions, generally between. Acids typically produce hydrogen ions (h+) when dissolved in water, which gives them their acidic properties. These ions are called cations. Sodium easily loses one electron to achieve a. Ions formed from sodium atoms have a charge of +1.
Explainer Ions and radicals in our world
Sodium easily loses one electron to achieve a. Ionic compounds are formed by ionic bonds from the electrostatic attraction of positively and negatively charged ions, generally between. How many protons and electrons does a neutral. What ions are present in acids? No, sulfuric acid does not have a dative bond.
Acids Typically Produce Hydrogen Ions (H+) When Dissolved In Water, Which Gives Them Their Acidic Properties.
Ionic compounds are formed by ionic bonds from the electrostatic attraction of positively and negatively charged ions, generally between. Ions formed from sodium atoms have a charge of +1. How many protons and electrons does a neutral. Sodium easily loses one electron to achieve a.
These Ions Are Called Cations.
Sulfuric acid is a strong acid that typically dissociates into hydronium ions and. What ions are present in acids? How are positive ions formed (what is gained or lost)? Use potassium (k) as an example.

..jpg)